Explain the origins of the term ‘beryl spaghetti models’.
The term “beryl spaghetti models” originated in the early 20th century, when scientists began to use beryl crystals to study the structure of molecules. Beryl is a mineral that is composed of beryllium, aluminum, and silicate, and it has a hexagonal crystal structure. When scientists used X-rays to study the structure of beryl crystals, they discovered that the atoms in the crystals were arranged in a regular, repeating pattern. This pattern resembled the strands of spaghetti, and so the scientists began to refer to these models as “beryl spaghetti models”.
Over time, the term “beryl spaghetti models” came to be used more generally to refer to any type of molecular model that is made from a material that has a regular, repeating crystal structure. These models are often used to study the structure of molecules in order to understand their properties and behavior. Beryl spaghetti models are still used today, and they are an important tool for scientists in a variety of fields.
Key figures or events associated with its development
Some of the key figures associated with the development of beryl spaghetti models include:
- William Henry Bragg and William Lawrence Bragg: Father and son who developed the Bragg’s law of X-ray diffraction, which is used to determine the structure of crystals.
- Max von Laue: German physicist who first discovered X-ray diffraction in 1912.
- Maurice de Broglie: French physicist who proposed the wave-particle duality of matter in 1924.
- Erwin Schrödinger: Austrian physicist who developed the Schrödinger equation in 1926, which is used to describe the wave function of a particle.
Some of the key events associated with the development of beryl spaghetti models include:
- 1912: Max von Laue discovers X-ray diffraction.
- 1913: William Henry Bragg and William Lawrence Bragg develop Bragg’s law of X-ray diffraction.
- 1924: Maurice de Broglie proposes the wave-particle duality of matter.
- 1926: Erwin Schrödinger develops the Schrödinger equation.
- 1930s: Beryl spaghetti models are first developed.
Describe the characteristics and applications of beryl spaghetti models.
Beryl spaghetti models are a type of computational model that is used to simulate the behavior of complex systems. They are named after the physicist and mathematician Beryl Mayne, who first developed the concept in the 1950s. Beryl spaghetti models are composed of a network of nodes and edges, where the nodes represent the individual components of the system and the edges represent the interactions between them.
Beryl spaghetti models are used in a wide variety of fields, including physics, biology, economics, and social science. They are particularly well-suited for modeling systems that are complex and difficult to understand, such as the human brain or the global economy. Beryl spaghetti models can be used to simulate the behavior of these systems under different conditions, which can help researchers to understand how they work and how to improve them.
Structure and components of beryl spaghetti models
Beryl spaghetti models are composed of a network of nodes and edges. The nodes represent the individual components of the system, and the edges represent the interactions between them. The nodes can be anything, from atoms to molecules to people. The edges can represent any type of interaction, from physical forces to chemical reactions to social relationships.
The structure of a beryl spaghetti model is determined by the specific system that it is being used to simulate. However, there are some general principles that apply to all beryl spaghetti models. First, the model must be large enough to capture the essential features of the system. Second, the model must be detailed enough to accurately represent the interactions between the components of the system. Third, the model must be computationally efficient so that it can be run on a computer.
Applications of beryl spaghetti models
Beryl spaghetti models are used in a wide variety of fields, including physics, biology, economics, and social science. They are particularly well-suited for modeling systems that are complex and difficult to understand, such as the human brain or the global economy. Beryl spaghetti models can be used to simulate the behavior of these systems under different conditions, which can help researchers to understand how they work and how to improve them.
Here are some examples of successful implementations of beryl spaghetti models:
- In physics, beryl spaghetti models have been used to simulate the behavior of atoms and molecules. These models have helped researchers to understand the structure of matter and the forces that hold it together.
- In biology, beryl spaghetti models have been used to simulate the behavior of cells and organisms. These models have helped researchers to understand the processes of life and how diseases develop.
- In economics, beryl spaghetti models have been used to simulate the behavior of the global economy. These models have helped researchers to understand the causes of economic crises and how to prevent them.
- In social science, beryl spaghetti models have been used to simulate the behavior of human societies. These models have helped researchers to understand the causes of social conflict and how to promote peace.
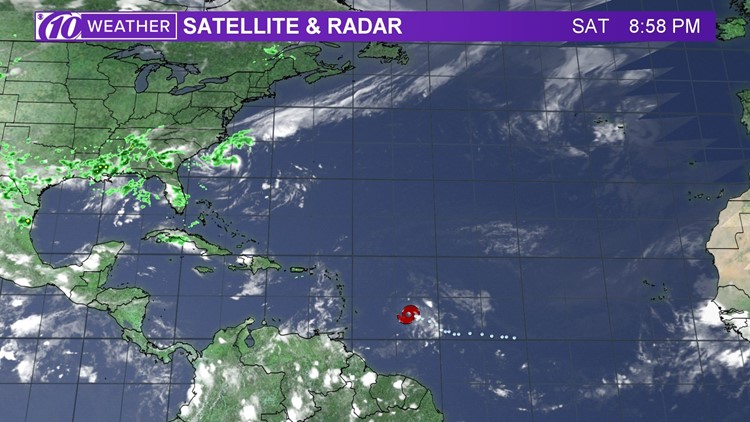
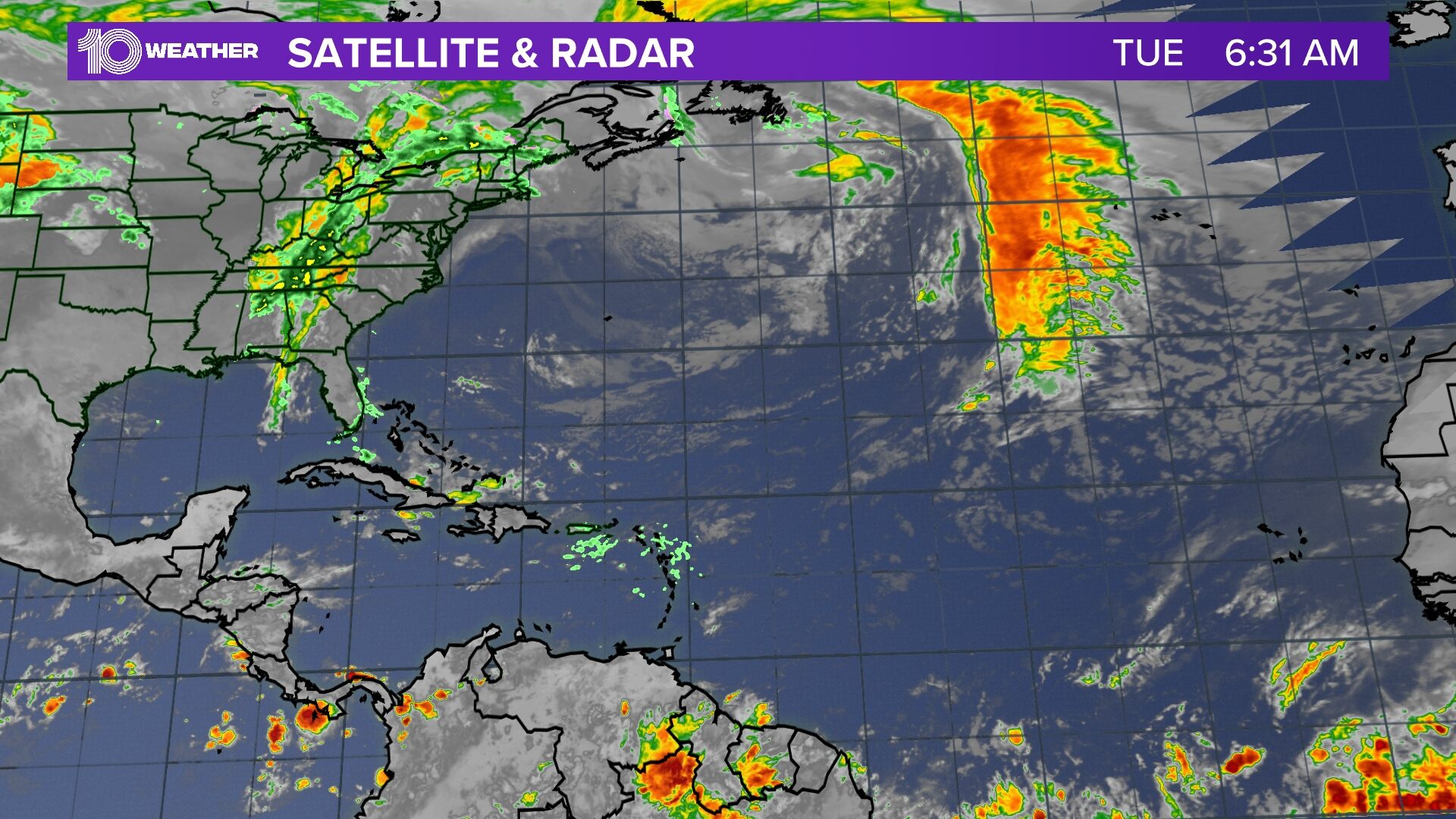
Beryl spaghetti models are essential tools for predicting the path of a hurricane. These models use a variety of data to create a range of possible tracks for the storm. By studying the spaghetti models, meteorologists can get a better idea of where the hurricane is likely to go and how strong it is likely to be.
For more information on the beryl hurricane track, please visit this website. Spaghetti models are an important part of hurricane forecasting, and they can help us to be better prepared for these storms.
Beryl spaghetti models, also known as spaghetti plots, provide a visual representation of potential hurricane tracks. These models are used by meteorologists to forecast the likely path of a hurricane, and they can be found on the beryl hurricane track website.
By analyzing the spaghetti models, meteorologists can make more informed predictions about the hurricane’s movement and intensity, helping to keep communities safe.